Income Tax Table
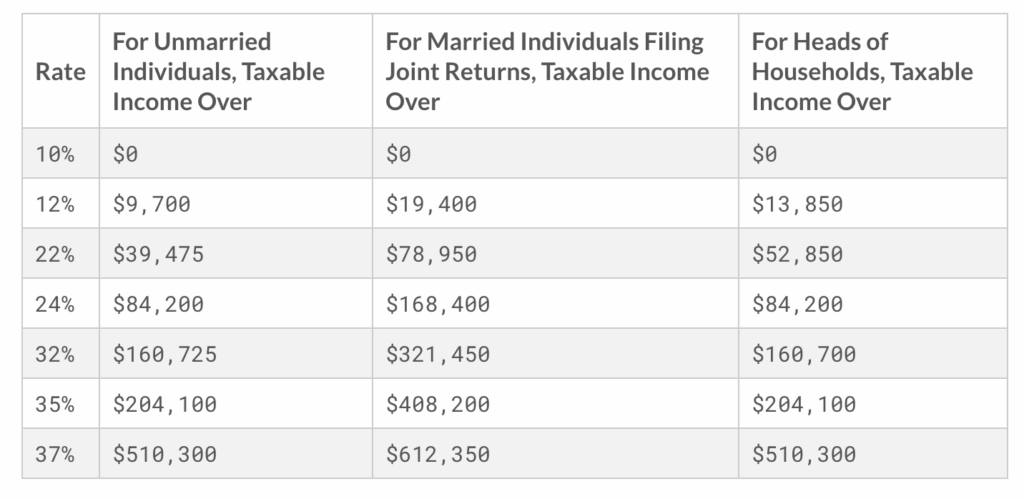
You’ll need an income tax table to follow along with the examples. Here’s a very succinct version of the 2019 Income Tax Table used in the examples below. (The actual standard deduction used below is rounded for simplicity. The real values for 2019 are $12,200 for single, $18,350 head of household, and $24,400 for married filing jointly).
Tax Calculation Example (One Tax Bracket)
For income tax, first, you’ll take your net income (don’t subtract any SE tax) and subtract your standard deduction (12K single, 18K head of household, 24K married). The amount leftover is subject to income tax corresponding to the income tax brackets (but, of course, there is a bit more to do if we want to get a more exact number). For example, if I was single, and made 21K, I would take 21K -12K (standard deduction) = 9K. If it was all self-employment earnings, I would owe SE tax on all of it ($2,967). We are allowed to adjust our taxable income by half of the SE tax owed ($1,484). The amount of our earnings actually subject to income tax would be $7,516 (that falls in the 10% bracket). Our income tax would be $752.
Tax Calculation Example Across Two Tax Brackets
Now a quick example which will span two tax brackets. Single with SE earnings of 28K. 28K-12K = 16K – $1,978 (1/2 SE tax) = $14,022. The first $9,700 is subject to the 10% tax bracket, so we will owe $970 on that amount. $14,022-$9,700 = $4,322 is subject to the next tax bracket of 12% ($519), for a total income tax due of $1,489.
Now What?
Once you have your total amount of tax due, you can then add in any credits. If you have a child, you get a 2K nonrefundable credit (up to $1,600 of that can be refundable). You can also look up the Earned Income Credit and see what amount of that credit you may be able to claim.
Misc. Notes/Comments
I kept SE tax and income tax separate in my examples. The total tax due (income + SE) in the first example would be $3,719. The total tax due in the second example would be $5,445.
Need a Refresher on Self-employment Taxes?
If you need a refresher on self-employment taxes, go ahead and check out our blog post here. For a refresher on the sliding income tax bracket concepts, check out that blog post here.
Contact Us
If you’re finding taxes and calculating what you may owe, please feel free to reach out to us at Chad@YourTaxPrep.com. You can also check out our pricing and consultation services if you’re interested in joining our close-knit tax family. Thank you for checking out our posts!
Recent Comments